How it works (flow diagram)
SuperTokens provides session management out of the box. We prevent many session attack vectors like:
- XSS (by using
httpOnlycookies) - Minimises damage from access token signing key compromise.
- Minimises damage from session data theft from database.
- Reliable detecting of session hijacking.
- CSRF attacks
- Brute force attacks
- Session fixation
caution
Depending on your application setup, sessions with cookies may not work on certain browsers like Safari which disable cross domain cookies by default.
To know if this is going to be a problem for you, please see this GitHub issue (which also contains proposed solutions).
You can also find one of the solutions here.
Overview of session flow#
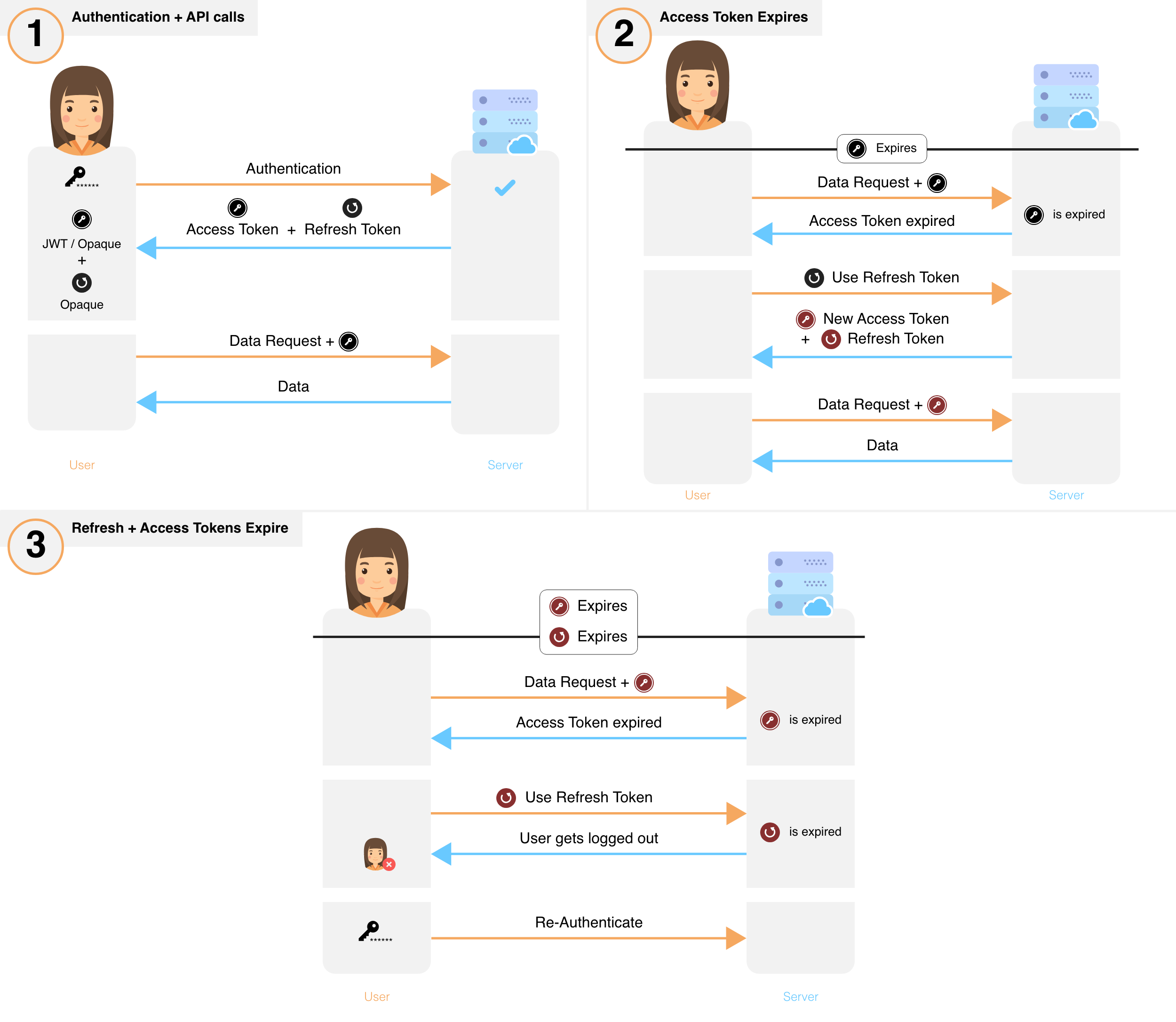
- After sign in, a new session is created by issuing a refresh and access token to the frontend.
- The frontend sends the access token for each API call that requires session authentication.
- These API calls verify the access token and its expiry. If verification fails, the API throws a session expired error, else, execution continues.
- If an API throws session expired error, the frontend uses its refresh token to get a new refresh and a new access token. This is done via a special API on your backend. If a session has been revoked, this API will also throw session expired after which the user will have to login again.
- After obtaining a new set of tokens, the frontend retries the original API call, yielding the desired result.
- To revoke a session, the backend removes the refresh token and its session information from its database.
 supertokens-auth-react
supertokens-auth-react